Type 2 Diabetes: The Pathway to Becoming a Healthy Diabetic
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
defining diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease characterised by high blood sugar that results from insulin resistance (CDC, 2021). In order to obtain a comprehensive understanding of what that statement means, we will need to break it down into its component parts.
Chronic Diseases
The Health Service Executive (HSE) defines chronic diseases as “long term conditions which can be treated but not cured” (The Health Service Executive, 2008). This means that although management and treatment of type 2 diabetes is possible, it is still impossible to fully cure yourself of diabetes. Moreover, most chronic diseases can not be passed on from person to person (University of Nevada, n.d.). Diabetes is one of those non-communicable diseases, where patients can not transmit the disease to others.
High Blood Sugar and Diagnostic tests
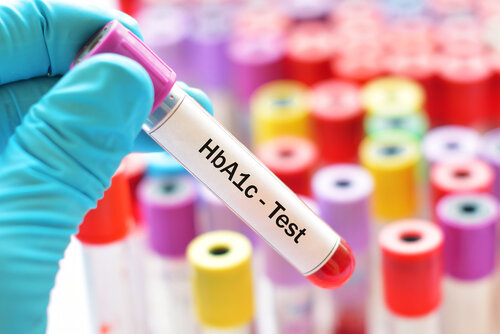
Type 2 diabetes is normally diagnosed with a glycated haemoglobin (A1C) test, which shows the average blood sugar of a patient across two to three months (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). A result below 5.7% is normal, while 5.7% to 6.4% is prediabetes and 6.5% or higher on two separate A1C tests indicates diabetes (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). Alternatively, doctors may use other tests such as random blood sugar tests, fasting blood sugar tests or oral glucose tolerance tests in the scenario that an A1C test is unavailable or a patient has conditions that interfere with an A1C test (MayoClinic.org, n.d.).
This is an example of an A1C test tube. Resulting values below 5.7% are normal, while values between 5.7-6.4% are prediabetic and anything above 6.5% across two tests indicates diabetes (MayoClinic.org, n.d.).
Insulin resistance and risk factors
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include being older, less active, stressed and/or obese. Alternative risk factors also include high blood pressure, high levels of fats (triglycerides) and high density lipoprotein (HDL) in the blood. In addition to these risk factors, it is very important to note that type 2 diabetes has a strong genetic link and 80-90% of diabetes patients have a family history of diabetes. Ultimately, these risk factors help contribute towards the body’s inability to respond to insulin and inability to secrete enough insulin from the pancreas. Due to the wide range of genetic causes, some individuals may be better treated through dietary changes alone, while others may respond better to medication. (Anon., n.d.)
Becoming a Healthy Diabetic
Lifestyle changes
The primary dietary change that diabetics should do is to control their carbohydrate intake. Carbohydrates have a great effect on your blood glucose levels, increasing it after consumption (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). Examples of carbohydrates include fruits, sweets, grains, rice and potatoes (Harvard TH Chan, n.d.). In addition, smaller portion sizes and consuming fewer calories daily can also help in treating diabetes (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). Weight loss can also greatly assist you in controlling your blood sugar. If an overweight person loses 5% of their bodyweight that is enough to see great benefits in blood sugar levels (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). The more weight that is lost, then the more benefits that will be seen (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). Furthermore, limiting inactivity and including resistance and aerobic exercises can also result in more stable blood sugar levels (MayoClinic.org, n.d.).
Medication and treatment
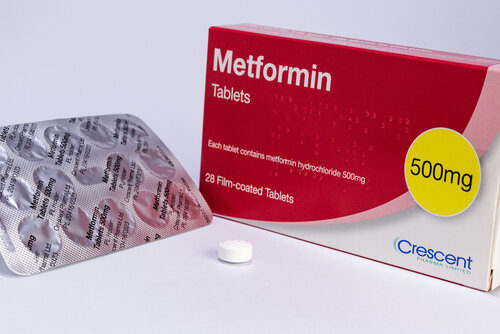
Metformin is the most common medication used for type 2 diabetes treatment (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). It lowers blood glucose levels in the liver, increasing the sensitivity your body has to insulin (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). Other medication also include sulfonylureas (helps body secrete more insulin), glinides (stimulates insulin secretion), thiazolidinediones (increases insulin sensitivity) and DPP-4 inhibitors (reduce blood sugar levels) (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). Some patients may also be prescribed insulin. Insulin is normally given when the patient cannot meet blood sugar targets from lifestyle changes or other treatment (MayoClinic.org, n.d.). Herbal remedies (such as apple cider vinegar, aloe vera or cinammon) can also be used, however it should be used in addition to conventional treatments and not alone (Greenman, 2018). Moreover, all treatments, herbal or not, should be discussed with a suitable medical professional before commencement (Greenman, 2018).
Metformin tablets are normally given with a 500mg or 850mg starting dose, 2 to 3 times daily for adults (Milpharm Ltd., 2020).
Complications of type 2 diabetes
Complications of type 2 diabetes result from persistently high blood sugar levels. This can lead to macrovascular (enlarged blood vessels), which results in higher risk of serious artery disease (Diabetes.ie, n.d.). In addition, diabetes can result in atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, myocardial infarctions and strokes (Diabetes.ie, n.d.). It can also cause diabetic retinopathy, a complication that causes damaging of the retina (back of the eye), eventually resulting in blindness if left untreated (Diabetes.ie, n.d.). Peripheral vascular disease can cause lower limbs to lose circulation (Diabetes.ie, n.d.). Drugs or exercise programs normally help prevent peripheral vascular disease, however in some cases it unfortunately results in the need of lower limb amputation (Diabetes.ie, n.d.).
the mentality of a healthy diabetic
Many newly diagnosed diabetics have issues accepting their diagnosis (APA, 2013). This results in feelings of guilt, disbelief and anxiety as a consequence (APA, 2013). Moreover, type 2 diabetics are twice as likely to become depressed in comparison to others (APA, 2013). This all indicates how difficult it is for diabetics to maintain mental wellbeing. The American Psychological Association (APA) states that diabetics should ensure they are very knowledgable about diabetes, so that they can make informed decisions about their illness and lifestyle (APA, 2013). They reaffirm the importance of maintaining a balanced view of their disease so that they do not just focus on it solely and develop strong support networks among their family and friends so that they can be supported during their stressful periods (APA, 2013). Diabetics may have negative feelings about their illness, but maintaining a balanced attitude throughout their lives can help ensure they live a stress-free and healthy life (APA, 2013).
Bibliography
Anon., n.d. What is Type 2 Diabetes?. [Online]
Available at: https://dtc.ucsf.edu/types-of-diabetes/type2/understanding-type-2-diabetes/what-is-type-2-diabetes/
[Accessed 15 July 2021].
APA, 2013. Taking control of your diabetes. [Online]
Available at: https://www.apa.org/topics/chronic-illness/control-diabetes
[Accessed 15 July 2021].
CDC, 2021. Type 2 Diabetes. [Online]
Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html
[Accessed 13 July 2021].
Diabetes.ie, n.d. Complications. [Online]
Available at: https://www.diabetes.ie/living-with-diabetes/living-with-type-2/complications-2/
[Accessed 15 July 2021].
Greenman, D. E., 2018. Natural Remedies for Type 2 Diabetes. [Online]
Available at: https://www.stamfordhealth.org/healthflash-blog/integrative-medicine/type-2-diabetes-natural-remedies/
[Accessed 15 July 2021].
Harvard TH Chan, n.d. Carbohydrates. [Online]
Available at: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/#:~:text=What%20are%20carbohydrates%3F,sugars%2C%20fibers%2C%20and%20starches.
[Accessed 15 July 2021].
MayoClinic.org, n.d. Type 2 diabetes. [Online]
Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351199
[Accessed 13 July 2021].
Milpharm Ltd., 2020. Metformin 500mg tablets. [Online]
Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/594/smpc#gref
[Accessed 15 July 2021].
The Health Service Executive, 2008. HSE Transformation Programme …. to enable people live healthier and more fulfilled lives. [Online]
Available at: https://www.hse.ie/eng/about/who/population-health/population-health-approach/population-health-chronic-illness-framework-july-2008.pdf
[Accessed 13 July 2021].
University of Nevada, R., n.d. Chronic Disease vs. Communicable Disease: What’s The Difference?. [Online]
Available at: https://onlinedegrees.unr.edu/blog/chronic-disease-vs-communicable-disease-whats-the-difference/
[Accessed 13 July 2021].